
The standard SI unit is kilograms per cubic meter ( kg/m 3). In other words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance. It is an intensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume: Typical densities of various substances at atmospheric pressure.ĭensity is defined as the mass per unit volume. How does the atomic mass determine the density of materials? Density of Helium The atomic mass number determines especially the atomic mass of atoms. The mass number is different for each different isotope of a chemical element. For 63Cu, the atomic mass is less than 63, so this must be the dominant factor. A nucleus with greater binding energy has lower total energy, and therefore a lower mass according to Einstein’s mass-energy equivalence relation E = mc 2. The nuclear binding energy varies between nuclei.This increases the mass of nuclei with more neutrons than protons relative to the atomic mass unit scale based on 12C with equal numbers of protons and neutrons.
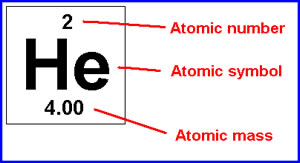
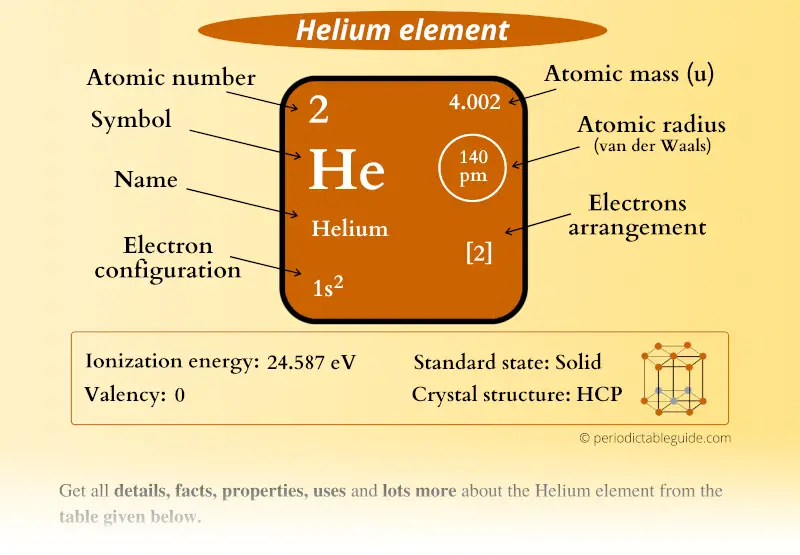
The neutron is slightly heavier than the proton.There are two reasons for the difference between mass number and isotopic mass, known as the mass defect: For example, 63Cu (29 protons and 34 neutrons) has a mass number of 63, and an isotopic mass in its nuclear ground state is 62.91367 u. For other isotopes, the isotopic mass usually differs and is usually within 0.1 u of the mass number. One unified atomic mass unit is approximately the mass of one nucleon (either a single proton or neutron) and is numerically equivalent to 1 g/mol.įor 12C, the atomic mass is exactly 12u, since the atomic mass unit is defined from it. One atomic mass unit is equal to 1.66 x 10 -24 grams. The unit of measure for mass is the atomic mass unit (amu). Therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occurring isotopes and their abundance. Note that each element may contain more isotopes. How does the atomic number determine the chemical behavior of atoms? Atomic Mass of Helium Since the number of electrons is responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. As the other answers explain because of its mass it will be practically in the nucleus( before decaying), and its shell might be be named as a K shell, but in a strict shell vocabulary the electrons will be in an L shell, as the next occupied orbital.Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure. The answer is yes, but this can happen on the same atom with the muons on their own orbital to the nucleus. You cannot just add two muons to an atom without changing the potentials that calculate the orbitals, so itĭo muons have different atomic shells than electrons? The displacement of electrons will happen to the outer orbitals and only x-rays and harder radiation can hit out an electron from a K shell (the closest orbital to the nucleus) because they are very tightly bound. One must not confuse orbitals of the solutions for muons or for electrons with the shells which count by the closest to the nucleus K, next L. If instead of electrons you have particles with the mass of muons ( mind you the muons will decay very fast and get out of the bound state) it will be different orbitals in dimensions. The K shell for electrons comes from solving the bound state for particles with the mass of the electrons. shells in atoms are a short hand way of describing the quantum mechanical complexity of the solutions for an atom.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
